
In 1967 “acute respiratory distress” was recognized and reported for the first time in the medical literature, 1 and PEEP was considered to be effective for improving oxygenation. For now, although functional differences among the different HFNC systems seem to be minor, to avoid adverse clinical events, it is essential to know the advantages and disadvantages of each element.įor hypoxemic respiratory failure, the frontline treatment is supplemental oxygen. Although the use of HFNC in adults who are critically ill has been dramatically increasing, the advantages and disadvantages of each element have not been well discussed. While NIV interfaces add to anatomic dead space, HFNC delivery actually decreases dead space.

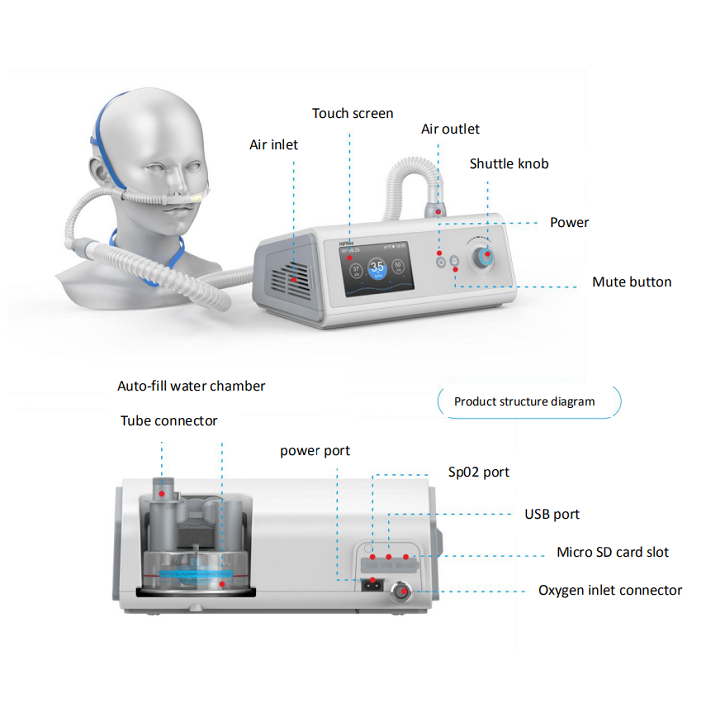
The HFNC system is simple: it requires only a flow generator, active heated humidifier, single heated circuit, and nasal cannula.

In the 2000s, less invasive high-flow nasal cannula (HFNC) therapy gained attention as an alternative means of respiratory support for patients who were critically ill. During the 1990s, noninvasive ventilation was found to be superior to invasive ventilation for exacerbations of COPD, acute cardiogenic pulmonary edema, and acute respiratory failure in patients who were immunocompromised.
Since ARDS was first described, mechanical ventilation via an endotracheal tube (invasive ventilation) has no doubt saved many patients. For hypoxemic respiratory failure, the frontline treatment is supplemental oxygen.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
